15990059518
1041301636@qq.com
No.9-3 Ankushan Community, Hezhen Town, Jiangshan City, Quzhou, Zhejiang Province
2023-04-13Tech Insights
I. Preface:
Plastic extrusion molding, such as UPVC (rigid polyvinyl chloride) profiles or pipe products, mainly through the mixing of PVC resin and related additives, extrusion molding, styling, traction, cutting and other links. The factors affecting the performance of the product cover every link of the production process, and the links interact and influence each other through the product as the media, and the problems in a certain link can be compensated by other links within a certain range, so that each link becomes an organism. Among them, raw materials, formulation equipment and operation process are the main factors of plastic extrusion molding, which directly affect the quality and output of extrusion molding.This paper focuses on the influence of extrusion equipment and raw materials on extrusion. Due to the polymer molding processing is affected by many factors, limited to my level and experience of the limitations of understanding, the one-sided views and mistakes in the article are inevitable, please criticize and correct.
2. UPVC raw material composition:
Generally speaking, UPVC raw materials are mainly composed of the following ingredients:
1. PVC resin:
Extruded PVC hard products generally use suspension method loose resin, S-PVC polymerization degree, particle size, porosity should be appropriate. Resin with large particle size difference and loose resin with compact particles should not be selected.
2. Stabilizer:
Because PVC resin is a heat-sensitive resin, when the temperature reaches about 90 ~ 130 ° C, the thermal degradation begins, the unstable HCL is removed, and the resin turns yellow. With the increase of temperature, the color of resin becomes darker, and the physical and chemical properties of the product decline. In addition to improving the production process of resin raw materials, it is mainly to add a stabilizer to PVC resin, absorb and neutralize HCL gas, and eliminate its catalytic degradation. Common stabilization systems are: lead salts, organotin, metal soaps and rare earth stabilizers.
3. Lubricants:
Additives for the purpose of improving lubricity and reducing interface adhesion. According to the function, there are external lubricant, internal lubricant and internal and external lubricant. The external lubricant can reduce the friction between the material and the metal surface to avoid the adhesion of the UPVC material to the barrel and screw after plasticization, and the internal lubricant can reduce the friction between the particles inside the material, weaken the cohesion between the molecules and reduce the melt viscosity. The use of lubricant has obvious effects on reducing screw load, reducing shear heat and increasing extrusion yield. The design of the lubricant in the formulation is very important.
4. Filling material:
In order to improve the hardness and rigidity of the product, reduce the deformation of the product and reduce the cost of raw materials, more CaCO3 filler is added in the production of UPVC products.
5. Process modifiers (ACR) :
Mainly to improve the processing of materials for the purpose of accelerating the plasticization of PVC resin, improve the flow of materials, thermal deformation and product surface gloss and other characteristics.
6. Impact modifier:
The main purpose is to improve the impact resistance of the product, improve the toughness of the product and improve the plasticizing effect. The commonly used modifiers for UPVC are CPE(chlorinated polyethylene) and acrylate impact modification.
Seven. Colorant:
Titanium dioxide, carbon black, etc.
Third, the plasticization mechanism of plastic extrusion equipment and the influence of formula composition on it:
There are many equipment for plastic extrusion molding, which are mainly used for the extrusion of UPVC hard products: exhaust single screw extruder and opposite direction twin screw extruder. The following is mainly to discuss the plasticizing mechanism of commonly used extruders for extruding UPVC products.
1. Exhaust single screw extruder:
1.1 Plasticizing mechanism:
Figure 1 shows the exhaust type single screw based on the ordinary single screw. Can be used for UPVC feeding powder molding extrusion and granulation.The screw is composed of two ordinary single screw in series, the length to diameter ratio is large (L/D=25 ~ 30), the first section of the single screw mainly through the material heat transfer, compression, melting homogenization play a role in the initial melting of the material, the second section of the single screw is mainly exhaust, further melting homogenization, the role of establishing extrusion pressure. From the exhaust port, the material should be in a semi-molten state, and the exhaust port is set in the conveying section of the rear screw.

The first screw is mainly a process of material conveying, compression and melting.
In the conveying section, the dry powder is gradually compacted to form a "solid bed" because the material temperature has not risen, only the air between and inside the powder particles is discharged.
In the compression section, the material temperature is about 160 ~ 170℃. With the reduction of the volume of the spiral groove, the gap between the material and the barrel surface is established to force the material to pass through the screw and the barrel. The increase of the pressure between the material and the barrel surface enhances the heat absorption effect of the material. Because the relative movement of the screw and the barrel accumulates and gradually increases in the front of the screw groove, the powder particles of the material in this section are broken and melted by shear. Because the shear force of the material in the screw groove is small, the plasticization consistency of the material in the screw groove is poor.
In the homogenizing section, the diameter of the screw bottom is reduced, so that the material in the middle of the screw groove is close to the barrel, prompting it to shear and heat to melt, further completing the melting of the material and making it uniform.
The bottom diameter of the conveying section of the rear screw (near the head) becomes larger, and its displacement is much larger than the homogenization section of the previous screw, where the material is not pressured into segments or large chunks, the gas and volatile components in the material are released, and the exhaust port is set here to discharge it through the vacuum pump. The material reaches the homogenization section through the second compression section, and the extrusion pressure is established under the action of the head, screw and barrel to form a dense and uniform material flow and extrude from the head. The displacement of the homogenization section here is greater than that of the previous section to prevent charging.
From the above analysis, it can be seen that the melting of single screw is mainly through the static of the screw rotating cylinder, the shear of the relative displacement of the material in different parts of the screw groove, the thermal compression of the material and the heat conduction between the cylinder and the screw to form a melt film melt pool, and the migration between the solid and liquid phase.

FIG. 2 Extrusion system of conical twin-screw extruder
Before discussing the plasticizing mechanism of conical twin-screw extruders, it is necessary to explain several concepts:
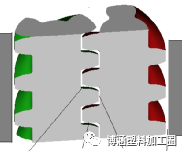
(1) C-shaped chamber: Figure 3, the volume contained by the inner surface of the barrel, the bottom cone of the screw, the two sides of the screw and the top surface of the connecting screw. The C-shaped chamber is a unique feature of the opposite-direction parallel twin screw extruder.
(2) Screw clearance δ1: FIG. 4, the radial clearance between the outer cone of the screw and the barrel on the cross section of the screw. Also known as spiral clearance.
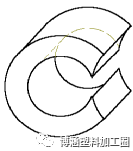
(3) Top gap (bottom gap) δ2: the gap between the top surface of the screw and the bottom surface of the rodding screw.
⑷ Side gap δ3: the gap between the edge surface and the groove surface.
(5) Tetrahedral gap: The wedge gap formed between the adjacent two screw tooth surfaces and the cone and the screw meshing line due to the change of screw tooth shape.
2.2.2 Plasticizing mechanism of materials of conical twin-screw extruder:
⑴ Conveying section:
The material enters the conveying section from the feeding port under the action of the screw forced driving force to transport forward, the screw each turn, the C-chamber material moves forward a lead, due to the structure, the volume of the C-chamber is getting smaller and smaller, the material is gradually pressed, because the contact pressure between the material and the barrel screw increases, the heat absorption increases, the material temperature gradually rises, preparing for the next step of melting. Due to the large surface area of the barrel and screw in the conveying section, the heat conduction efficiency between the barrel and screw is improved.
⑵ Preplasticizing section:
After the material is heated and compressed in the conveying section, most of the air between and inside the powder particles is discharged, and the material density increases. As the material in the C-shaped chamber continues to move forward, the material in contact with the barrel and screw is subject to adhesion to maintain the same speed as the barrel or screw, and the shear action under the drive of the screw is stronger than the material in the middle of the screw groove and the heating time is long and begins to melt, and the material in the C-shaped chamber is melted from the outside to the inside circulation. With the change of the volume of the C-shaped chamber, the exchange of materials inside and outside is enhanced. Some extruder manufacturers according to the characteristics of the extruder in the pre-plasticizing section set up a mixing tank, the purpose is to communicate before and after the C-shaped chamber material, enhance the shear effect, conducive to the exchange of C-shaped indoor outer materials, improve the melting effect. After the material passes through the preplasticization section, the large powder granular material is basically broken, and the material is in a semi-molten state.
(3) Plasticizing section:
Also known as compression section. The C-shaped chamber volume of this section is sharply reduced (the displacement of this section is only between 0.25 and 0.4 of the conveying section), and the materials are subjected to strong extrusion, shear and exchange effects when passing through.
⑷ Exhaust section:
The UPVC mixture enters the exhaust section after the conveying, pre-plasticizing and compression section. Since the C-shaped chamber volume of the exhaust section is much larger than that of the compression section (the general displacement is more than 3 times that of the compression section), the materials arrive at this section to reduce pressure, the materials form segments or large blocks, and the gases and low molecular volatile components in the materials are released. The exhaust port is set in this section. The gas is discharged through the exhaust port under the action of the vacuum pump. UPVC extrusion exhaust function is very important, otherwise, the bubbles in the product will seriously affect the mechanical properties.
⑸ Metering section:
Since the volume of C-shaped chamber in conveying section, pre-plasticizing section, plasticizing section and metering section is constantly changing, and the C-shaped chamber materials in each section of the screw head are different in number, and the materials enter the metering section after constantly changing positions, which is mainly to further plasticize and homogenize the materials and establish extrusion pressure under the action of the head. Due to the reduction of the volume of the C-shaped chamber in the metering section, the material is compressed again after homogenization to form a dense and uniform fluid through the coupling body (transition body), porous plate, and head extrusion.
Effect of various gaps on melting:
The material in the screw gap δ1, side gap δ3 and tetrahedral gap δ4 is subjected to strong shearing action due to the different velocity of movement with the metal surface in contact, and the smaller the gap, the stronger the shearing effect. The material in the top gap (bottom gap) δ2 is similar to the material in the two-roll smelting machine by extrusion and melting, the smaller the gap, the stronger the extrusion effect.
It should be noted that the gaps are too small or too large. Too small clearance increases the difficulty of manufacturing and has an adverse effect on the melting consistency of the material. If the gap is too large, the leakage flow increases, and the production efficiency of the extruder is reduced. When the ratio of the size of various gaps is reasonable, it is also beneficial to melting.
The influence of the ring groove on melting:
Most of the screw has a ring groove between the functional segments, in addition to the role of processing and cutting, the redistribution of C-shaped indoor materials is beneficial to promote the melting and homogenization of materials. Of course, the use of other ways (such as reflux tank) can meet the melt homogenization of the material, but also do not have a ring tank, such as the ARGOS 93 counterdirectional double extruder produced by the Austrian company CINCINNATI.
2.3 Plasticizing mechanism of parallel twin screw extruder:
The plasticizing mechanism of the different parallel twin screw extruder is basically the same as that of the cone twin extruder, the difference is that the diameter of the screw barrel is the same everywhere, the heat absorption area of the material in the feeding section is small, the diameter of the screw metering section is larger than that of the cone twin, and the screw speed cannot be too large. Therefore, in order to improve the plasticizing effect, the length-to-diameter ratio of the screw of the different parallel twin screw extruder is larger than that of the cone twin extruder (generally L/D=25 ~ 30). The volume size of the C-shaped chamber of the different parallel twin screw extruder is the same as that of the cone twin, and the change mode is basically the same. FIG. 5 shows the comparison of displacement of different directional flat twin screws with that of conical twin screws.
The transformation process of UPVC materials in the processing process is not only related to the composition of the mixed ingredients, but also has a great relationship with the external processing conditions. Such as the temperature of mixing ingredients, the order of mixing, the extrusion process temperature, the screw speed, the feeding amount and the strength of the material subjected to shear action. In the analysis of material plasticization degree should be considered comprehensively, overall analysis.
2.4 Influence of material formula on plasticization of twin-screw extruder:
Due to the different formula ingredients and dosage used by each manufacturer of UPVC products, the following is only an analysis of PVC resin and commonly used additives.
⑴ PVC resin:
Different types of PVC resin because of its different polymerization degree, different powder particle structure, different bonding strength between particles, different powder surface thickness, the external conditions required for melting are also different. The thin resin of PVC resin powder is easier to melt than the thick resin, and the loose resin is easier to melt than the dense resin. The large and compact particles of the material are not easy to plasticize and will form "fish eyes", affecting the appearance and performance of the product. The material with uniform powder size and uniform porosity has good melting uniformity, and the performance and appearance of the products produced are better.
(2) Stabilizer:
There are many kinds of stabilizers, which have different effects on the deformation and melting of materials in extrusion, and the synergistic effect of different stabilizers has obvious advantages. With the in-depth research on the stability mechanism of processing and molding of UPVC products, the compound stabilizer used in combination with the main and auxiliary stabilizers and lubricants is usually used in the formula.
The size of the amount of stabilizer added should first take into account the form and structural characteristics of the extruder and the mold used, when the material stays in the extruder and the mold for a long time, the amount of stabilizer added should be relatively large, and the stable dose should be relatively large when the shear effect is large. Generally speaking, the heating time of the cone double is shorter than that of the heterotropic flat double, and the heating time of the single screw is the longest. If the structure of the extrusion system of the same type of extruder is relatively different, the shear strength should be considered. When the mold runner is long and the volume is large, the material is heated for a long time, and this factor should also be considered when designing the formula, such as the stable dose of the production of large diameter pipes.
Secondly, the amount of stabilizer should consider the auxiliary lubrication effect, and the amount of various stabilizers changes due to their different lubrication effects on the material. The stabilizer material with strong lubrication effect is subjected to weak shear action, and the stabilizer dosage is appropriate and less. When the internal lubrication of the composite stabilizer is strong, it is beneficial to melt the material, and when the external lubrication of the composite stabilizer is strong, it is beneficial to reduce the screw load. Overall consideration should be given when determining the amount of compound lubricant.
The amount of stabilizer should also consider the influence of process temperature, extrusion screw speed, screw diameter and other factors, the process temperature setting is high, the amount of stabilizer is too large; High speed, large screw diameter and large stabilizer dosage.
(3) Lubricant:
The amount of lubricant added has obvious influence on the melting time, speed, screw load, extrusion yield, head pressure and mechanical properties of the product. A small change in the amount of lubricant will also affect the rheological behavior of the extruded material. The selection and dosage of lubricant is the key to UPVC formulation design.
Lubricants have internal lubricants, external lubricants and internal and external lubricants according to the function, and the internal lubricant can penetrate between the molecular chains of PVC particles after melting, reduce the intermolecular gravity, reduce the melt viscosity, and promote the plasticization of resin. The external lubricant can not enter the PVC particles after melting between the molecular chain, distributed between the PVC particles and materials and the surface of the barrel screw, the external lubrication dose increases, the material is subjected to small shear action, the initial melting time is delayed, the melting time is long, the screw load is reduced, the screw load is reduced to increase the feeding amount and improve the extrusion output.
When the lubrication dose is too much (especially the external lubricant), the impact resistance of the product is reduced, the lubrication film between the material and the cylinder is too thick, the material can not adhere to the inner surface of the cylinder, and the material is very weak under the shearing effect.
Table 1 Statistical table of parameters related to the formula torque rheological
test of profiles

From Table 1, it can be seen that the average time for the material to reach the maximum torque is from 46.67 seconds to 143.31 seconds, indicating that the time required for plasticizing is very different. The maximum torque varies greatly from 22.33N.M to 37.5N.m, indicating that the load subjected to the extruder processing is also very different. Because the load is different, it will affect the amount of feed, which will affect the extrusion output.
Four. In SUMMARY:
In this paper, the melting mechanism and formula adjustment of the material in the extruder are analyzed. Because of the high polymer processing and molding technology is very practical, the raw material formula, processing equipment and technological conditions of the product are different.
Therefore, the actual production should be combined with the structure of the production equipment, especially the extrusion system, the composition of the product performance requirements, the production capacity of a comprehensive analysis of the influence of each component of the auxiliary agent on the material melting, so as to determine a reasonable production process.